Asian shares fell and gold costs had been barely up early on Monday as threat sentiment soured and fears of a wider regional battle saved merchants on edge following Iran’s retaliatory assault on Israel over the weekend.
The greenback scaled a contemporary 34-year excessive towards the yen on rising expectations that sticky inflationary pressures within the United States will hold charges there increased for longer.
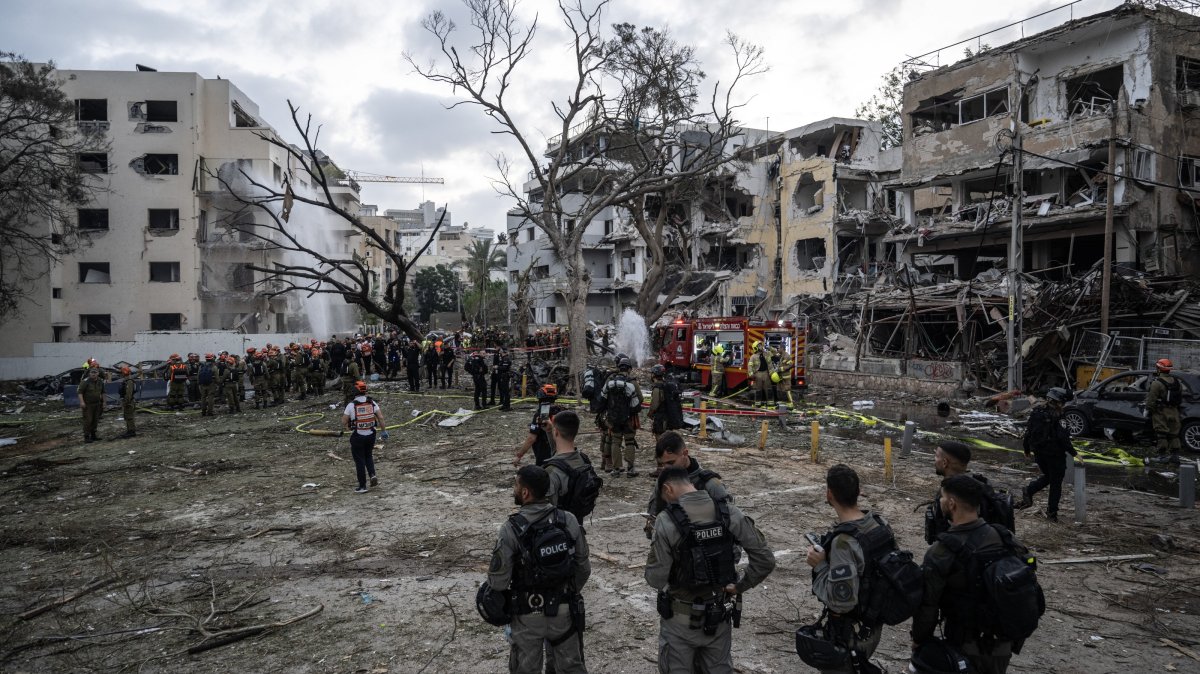
MSCI’s broadest index of Asia-Pacific shares exterior Japan fell 0.7% after Iran launched explosive drones and missiles at Israel late on Saturday in retaliation for a suspected Israeli assault on its consulate in Syria on April 1.
The menace of open warfare erupting between the arch Middle East foes and dragging within the U.S. has left the area on tenterhooks. U.S. President Joe Biden warned Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu that the U.S. is not going to participate in a counter-offensive towards Iran.
Israel mentioned, “The campaign is not over yet.”
A way of nervousness swept over Asian markets on Monday amid the escalating geopolitical tensions, with Japan’s Nikkei sliding 1%, whereas Australia’s S&P/ASX 200 index misplaced practically 0.5%.
Hong Kong’s Hang Seng Index was down 0.63%.
The flight to security despatched gold up greater than 0.5% to $2,356.39 an oz at 5 a.m. GMT and saved the greenback agency. At round 8:45 a.m. GMT, the gold traded at 2,358.80 per ounce.
Oil costs
Oil costs, nevertheless, hardly reacted to the news, as merchants had largely priced in a retaliatory assault from Iran that may doubtless additional disrupt provide chains. That noticed Brent 2.358,80 crude futures peaking at $92.18 a barrel final week, the best degree since October.
Brent was final 0.24% decrease at $90.23 per barrel, whereas U.S. West Texas Intermediate crude futures fell 0.35% to $85.36 a barrel.
“The key risks for the global economy are whether this now escalates into a broader regional conflict and the response in energy markets,” mentioned Neil Shearing, group chief economist at Capital Economics.
“A rise in oil prices would complicate efforts to bring inflation back to target in advanced economies, but will only have a material impact on central bank decisions if higher energy prices bleed into core inflation.”
U.S. inventory futures ticked increased after a heavy selloff on Wall Street on Friday as outcomes from main U.S. banks didn’t impress.
S&P 500 futures and Nasdaq futures every rose about 0.4%.
EURO STOXX 50 futures tacked on 0.22%, whereas FTSE futures slid 0.5%.
China, nevertheless, was an outlier, with shares pushing increased after the nation’s securities regulator issued draft guidelines on Friday to strengthen the supervision of firm listings, delistings and computer-driven program buying and selling.
Market members took the transfer as a constructive sign to enhance China’s ailing inventory market and defend buyers’ pursuits.
The nation’s blue-chip CSI300 index rose practically 2%, whereas the Shanghai Composite index gained 1.2%.
Rate rethink
Elsewhere, U.S. Treasury yields held close to their latest highs as merchants pared again their expectations of the tempo and scale of charge cuts from the Federal Reserve (Fed) this 12 months.
The benchmark 10-year yield final stood at 4.5605%, whereas the two-year yield held close to the 5% degree and was final at 4.9269%.
A continued run of resilient U.S. financial knowledge, significantly final week’s hotter-than-expected inflation report, has added to the view that U.S. charges might stay increased for longer and {that a} Fed easing cycle is unlikely to begin in June.
Futures now level to about 44 foundation factors price easing anticipated this 12 months, an enormous pullback from the 160 bps priced in firstly of the 12 months.
That sea change within the charge outlook has, in flip, despatched the greenback on a tear, pushing it to a 34-year peak of 153.85 yen on Monday.
The euro and sterling had been equally pinned close to five-month lows.
“We have updated our forecasts for the U.S. FOMC, pushing out the start of the interest rate cutting cycle to September 2024 from July previously,” mentioned Kristina Clifton, a senior economist at Commonwealth Bank of Australia.
“The U.S. CPI has been stronger than expected over the first three months of 2024. We expect that a string of inflation prints of 0.2%/month or lower will give the Fed confidence that inflation can stay sustainably lower and that interest rates do not need to remain at a restrictive level.”
A slew of Fed policymakers are as a consequence of communicate this week, together with Chair Jerome Powell, who might additional make clear the long run path of U.S. rates of interest.
The shift in charge expectations has halted Bitcoin’s blistering rally after the world’s largest cryptocurrency repeatedly notched contemporary data this 12 months because of flows into new spot bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and expectations of imminent Fed cuts.
Bitcoin fell over 3% to $65,010, partly weighed down by the worldwide risk-off temper.
Source: www.dailysabah.com